Calculate Your Soil Needs
Enter your garden details below to determine how much soil you’ll need
Your Results
💡 Soil Tips
For most garden plants, aim for 6-12 inches of quality soil. Root vegetables may need 12-18 inches. Always add organic matter to improve soil structure.
Garden soil is best for in-ground planting. For containers, use potting mix which provides better drainage and aeration.
Soil Calculation Report
Your personalized soil calculation results
Project Details
Calculation Results
- Calculate Your Soil Needs
- Soil Calculation Report
- What Is a Soil Calculator?
- Soil Calculator Basics: What, Why, and How
- How Soil Calculators Work: Step-by-Step
- Soil Calculation Formulas and Methods Explained
- Soil Types, Densities, and Why They Matter
- Specialized Calculations and Advanced Scenarios
- Practical Examples: Soil Calculator in Action
- Pro Tips for Getting the Most Accurate Results
- Soil Calculator Tool: Try It Now
- Calculate Your Soil Needs
- Soil Calculation Report
- Advanced Resources and Further Reading
- Conclusion
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What Is a Soil Calculator?
A soil calculator simplifies the process of calculating how much soil is needed for your gardening, landscaping, or construction project. It works by calculating the volume of soil based on the measurements you input. Why does it matter? If you're planting a garden or creating a raised bed, knowing the precise amount of soil helps you avoid wasting money or running out halfway through your project. With the right calculation, you'll get a healthier garden and a smoother, more cost-effective process.
Why Accurate Soil Measurement Matters for Gardening, Landscaping, and Construction?
You might think you can eyeball it, but using the right amount of soil is key to getting the results you want. Too little, and your plants won’t have enough room to grow; too much, and you're just wasting soil—and money. Whether you’re sprucing up your lawn, building raised beds, or tackling a construction project, a soil calculator helps prevent errors, saves time, and ensures your soil is applied just right. Getting it right the first time is a huge win for your garden and your budget.
Anyone involved in gardening or landscaping could use a soil calculator, from home gardeners to professional landscapers. If you're a contractor working on a project, or a DIYer tackling a home improvement job, this tool is a game-changer.
We'll guide you through the key steps of using a soil calculator in this guide. We’ll cover everything from measuring your space and entering the data to understanding your results. We'll also provide professional tips to help you achieve the most precise results, no matter the size of your project.
Soil Calculator Basics: What, Why, and How

What Does a Soil Calculator Do?
A soil calculator helps you determine how much soil you need by calculating the volume based on the area you’re working with. It takes measurements like length, width, and depth, and then it computes how much soil will fill the space. It’s not just about knowing the volume—it can also help estimate the cost, number of bags, and even the weight of the soil you’ll need. For anyone tackling a gardening or landscaping project, this tool is like a guide that keeps you on track.
Common Uses for Soil Calculators
Soil calculators are incredibly versatile. They’re used for projects like filling raised beds, landscaping a garden, or even installing new sod. Home gardeners use it for smaller projects, while landscapers and contractors rely on it for larger jobs. Whether you’re planting vegetables, flowers, or setting up a new lawn, the soil calculator helps ensure that your plants have the right amount of soil to grow strong and healthy. It’s a tool that saves time and helps prevent waste.
Benefits of Using a Soil Calculator
The biggest benefit is that it saves you money. By knowing exactly how much soil you need, you won’t have to buy extra bags or deal with excess material. It also keeps your project on track, helping you avoid running out of soil halfway through. Plus, it’s great for plant health. By getting the soil volume right, you ensure proper drainage, root development, and overall plant growth. Whether you’re a homeowner or a professional, a soil calculator is an easy way to plan, execute, and succeed.
How Soil Calculators Work: Step-by-Step
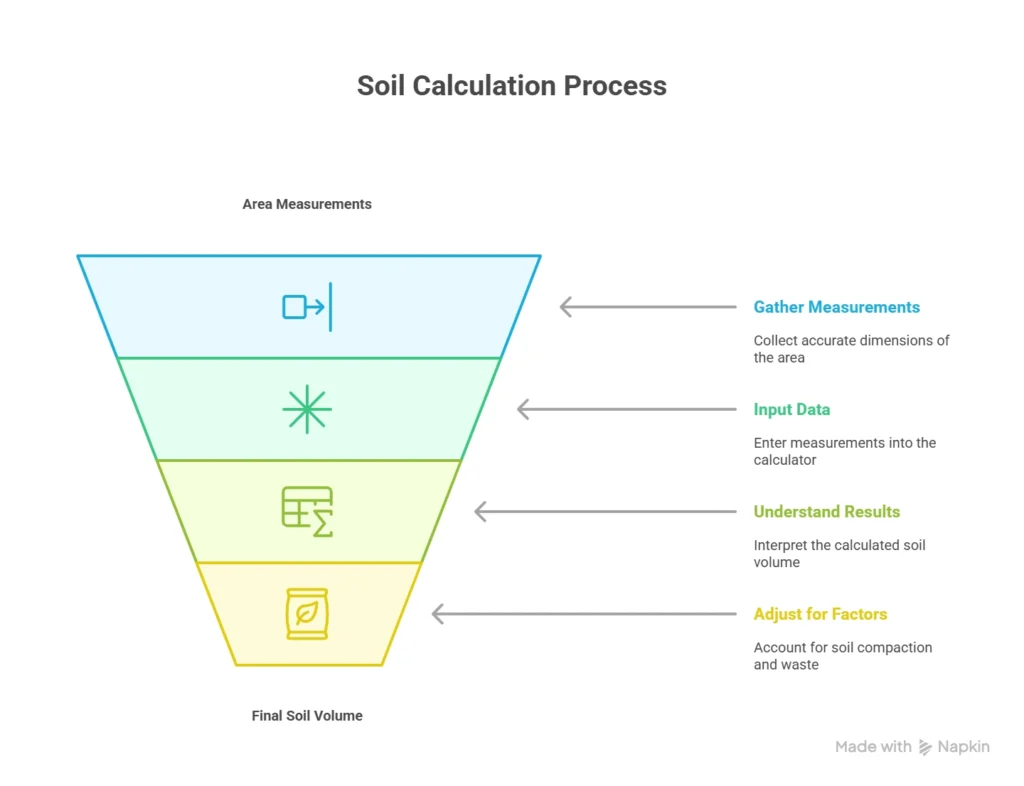
Step 1: Gather Your Measurements
To start using a soil calculator, the first thing you need to do is measure your space. This means taking accurate measurements of length, width, and depth. For a rectangular or square area, this is straightforward: simply measure each side. But if your area is more complex, like a circle or an irregular shape, break it down into smaller, simpler sections—like squares or circles. Then, compute the area of each and combine the totals. The more accurate your measurements, the more accurate your soil calculation will be.
Step 2: Input Your Data
Once you’ve taken your measurements, simply input them into the soil calculator. You can usually enter the measurements in various units like feet, inches, meters, or yards, depending on what you're comfortable with. Make sure you’re consistent with your units—don’t mix feet with inches, for example. Some calculators automatically handle unit conversions (like from cubic feet to cubic yards), so you don’t have to worry about doing math by hand.
Step 3: Understanding the Results
After you input your data, the calculator will show you the soil volume needed. The result will typically be in cubic feet, cubic yards, or liters. Some calculators also provide weight estimations or tell you how many bags of soil you’ll need to buy. This is especially useful if you’re buying pre-bagged soil, helping you avoid the guesswork at the store.
Step 4: Adjusting for Real-World Factors
Now that you have your soil volume, remember that not all soil settles the same. Some soil types, especially loose or organic materials, will compress or settle over time. It’s a good idea to add about 10–20% extra to account for soil compaction, settling, and waste. This ensures that you have enough soil even if things don’t go exactly as planned.
Soil Calculation Formulas and Methods Explained

Basic Volume Formula
The basic formula for calculating soil volume is simple: Length × Width × Depth. This works for rectangular or square areas. Just measure the length, width, and depth of your space, multiply them together, and voilà, you have your soil volume in cubic units (feet, yards, or meters, depending on what you're using). This formula is the foundation, and once you get the hang of it, you’ll be able to calculate soil needs for most basic projects.
Calculating for Different Shapes
Things get a bit trickier when you’re dealing with circles, odd-shaped plots, or other irregular spaces. For circles, you can use the formula for the area of a circle: π × radius². Once you have the area, multiply it by the depth to get the volume. For irregular areas, you can break the space into smaller, easier-to-manage sections, calculate the volume for each, and then add them all together. It might take a little more effort, but it’s worth it for accurate results.
Advanced Methods
For larger or more complex spaces—like sloped areas or multi-layered projects—you may need to use more advanced methods. One common approach is the grid method, which involves dividing the area into a grid of smaller squares and calculating the volume of each. Another method is the end area method, which works well for areas that taper or have varying dimensions. For these advanced projects, soil calculators can be a huge time-saver by doing the heavy lifting of the calculations for you.
Bagged Soil Conversion
If you’re buying bagged soil, you’ll need to convert your calculated volume into the number of bags you’ll need. Typically, a standard soil bag holds about 1 cubic foot of soil, but it can vary. Most soil calculators offer a way to convert your cubic volume into the number of bags, so you can easily figure out how much to purchase. This makes planning a lot simpler, especially if you’re buying retail bags and want to avoid over or under-buying.
Soil Types, Densities, and Why They Matter
Overview of Soil Types
Not all soil is created equal. Different soil types have unique characteristics that affect both plant growth and the amount of soil you'll need. Common soil types include loam, clay, sand, silt, peat, and chalk. Loam is perfect for most plants as it drains well yet retains moisture, whereas clay is heavy and water-holding, and sand drains too rapidly. Peat is great for acid-loving plants, and chalk soil tends to be alkaline. By knowing your soil type, you can choose the appropriate plants and amendments to ensure a thriving garden or landscape.
Soil Density and Bulk Density
Soil density, specifically bulk density, is crucial for calculations. Bulk density is the ratio of soil weight to its volume. It’s important because soil that’s denser will weigh more and take up less space. For instance, clay has a higher bulk density than loam, meaning you'll need more space to store the same weight of soil. When calculating how much soil you need, understanding density helps make your measurements more accurate and ensures the right amount for your project.
How Soil Type Affects Volume and Weight
Soil type influences both the volume and weight of the soil you'll need. Loam is typically lighter and easier to work with, while soil with a high clay content is denser and more compact. If your project uses a soil type that’s denser, like clay or sandy loam, you may need fewer cubic yards to fill a given space compared to using lighter soils like peat or pure sand. Adjusting your soil calculator for the right type ensures that you're not over or underestimating the material required.
Expert Tip:
Testing your soil type at home is easy and can make a big difference in your planning. Take a small sample and moisten it with water, then squeeze it in your hand. If it forms a ball that doesn’t crumble, it’s likely clay. If it breaks apart easily, it’s sand. Loam will hold together without being too sticky or dry. This quick test can help you fine-tune your soil needs and adjust your calculations for the best results.
Specialized Calculations and Advanced Scenarios

Calculating for Raised Beds, Planters, and Containers
When it comes to raised beds or container gardening, the depth of your soil matters a lot. For vegetables, a good depth is around 12 inches, while flowers and shrubs might need 6–8 inches. To calculate soil for raised beds or planters, simply measure the length, width, and depth, just like a regular space, and calculate the volume. But keep in mind that the soil in containers or raised beds can compact faster due to limited space for expansion. Make sure to account for this by adding a little extra soil to prevent settling.
Sloped, Irregular, or Multi-Layered Areas
If your garden or project area is on a slope or has multiple layers (like terraced hills), you’ll need to approach calculations differently. For sloped areas, you can use the same basic formula but adjust the depth based on the slope's angle. When dealing with an irregular space, split it into smaller, manageable areas. For multi-layered areas, calculate each layer’s soil requirement separately and then combine the totals. These calculations might take a bit more effort, but they’ll ensure accuracy in even the trickiest spaces.
Swell and Compaction Factors
Soil doesn’t always stay in the same form from delivery to installation. When soil is transported, it can be loose, but once placed, it may compact. Soil compaction reduces the volume of soil, so it's important to account for this. Add 10–20% more soil to allow for swelling during installation, especially if you’re using organic soil mixes like compost or mulch. This extra amount ensures that you’ll have the right depth and volume once everything settles into place.
Soil Blending and Amendments
In some cases, multiple types of soil are required. For optimal plant growth, you might need a blend of different materials like topsoil, compost, and sand. To calculate a custom soil mix, measure the amount of each ingredient needed for your space. For example, if you want a 50/50 blend of topsoil and compost for a garden bed, simply calculate the volume for each material separately and then combine them. This method is perfect for creating a balanced soil environment tailored to your specific plants and project needs.
Practical Examples: Soil Calculator in Action

Example 1: Calculating Soil for a Rectangular Raised Bed
Let’s say you’re setting up a raised bed that’s 4 feet long, 3 feet wide, and 1 foot deep. Using the basic volume formula, you simply multiply these dimensions together: 4 × 3 × 1 = 12 cubic feet of soil. If you’re using bagged soil and each bag holds 1 cubic foot, you’ll need 12 bags. This is an easy calculation that gives you exactly what you need without any guesswork.
Example 2: Estimating Soil for a Circular Flower Bed
Now, if you want to fill a circular flower bed with a radius of 5 feet and a depth of 6 inches, you need to adjust your formula. Start by calculating the area of the circle: π × 5² = 78.5 square feet. Next, multiply the area by the depth (in feet): 78.5 × 0.5 = 39.25 cubic feet of soil. You’ll need a bit more soil because of the circle’s shape, and with this calculation, you can easily figure out the volume to buy.
Example 3: Multi-Bed Garden Project (with a downloadable/printable worksheet)
Let’s say you have three garden beds: one rectangular (5 x 3 x 1 feet), one square (4 x 4 x 1 feet), and one circular (radius 6 feet, depth 0.5 feet). First, calculate the volume for each bed
Rectangular bed: 5 × 3 × 1 = 15 cubic feet
Square bed: 4 × 4 × 1 = 16 cubic feet
Circular bed: π × 6² × 0.5 = 56.5 cubic feet
Total: 15 + 16 + 56.5 = 87.5 cubic feet. You can use a worksheet to keep track of these numbers for easy reference.
Example 4: Converting Volume to Bags for Retail Purchase
Let’s say you’ve determined that 50 cubic feet of soil are required for your project. Since each bag contains 1.5 cubic feet, divide 50 by 1.5 to find the number of bags: 50 ÷ 1.5 = 33.33 bags. Round up, and you’ll need 34 bags to complete your project. This helps you avoid the hassle of running out of bags or buying extra that you don’t need.
Pro Tips for Getting the Most Accurate Results

Measuring Tips and Common Mistakes to Avoid
When measuring for a soil calculation, it's important to be precise. One common mistake is not measuring the depth of the area correctly, especially if the surface is uneven. Always measure the deepest point of your area, especially for irregular spaces. Another mistake is mixing up units (feet with inches, for example). To avoid errors, stick to one unit system throughout. Double-check your measurements and be sure to add a little extra for settling—this is especially important for loose or organic soil mixes.
Allowing for Soil Settlement and Waste
Soil tends to settle over time, especially when it's disturbed or compacted. When ordering soil for a project, it’s smart to add 10–20% more to your total volume estimate. This extra amount accounts for soil compaction and settling once it’s in place. Also, remember that not all soil deliveries are perfectly precise, so some of it may end up being wasted due to spills or incorrect measurements. Plan for a little cushion to ensure you don't come up short.
When to Consult a Professional
If you're dealing with a large-scale project, especially one involving irregular terrain or complex landscaping, it may be worth consulting a professional. They can help refine your calculations and ensure you're using the best soil for your specific needs. Contractors, landscapers, or gardening specialists can also advise on soil density, compaction, and custom mixes that may be necessary for optimal growth or construction stability.
How to Use Soil Calculators for Large-Scale Projects
For larger projects, the soil calculator is an even more valuable tool. Whether you're landscaping a backyard, planning a new lawn, or working on a commercial project, the calculator will help you determine how much material you need, saving time and reducing costs. For complex projects, break the area into manageable sections, calculate the volume for each, and then add them together. Many online soil calculators allow you to input multiple areas at once for streamlined calculations. This way, you can avoid over-purchasing or wasting materials.
Soil Calculator Tool: Try It Now
Interactive Soil Calculator Widget
Now that you've learned all about how soil calculators work and why they’re essential, it’s time to put your knowledge into action! Enter your details into the interactive soil calculator below to instantly find out how much soil you'll need for your next project. Whether you're filling raised beds, creating a new garden, or preparing a large landscaping area, this tool will give you accurate results at your fingertips. Simply input your measurements, and the calculator will do the math for you—no stress, no hassle.
Calculate Your Soil Needs
Enter your garden details below to determine how much soil you'll need
Your Results
💡 Soil Tips
For most garden plants, aim for 6-12 inches of quality soil. Root vegetables may need 12-18 inches. Always add organic matter to improve soil structure.
Garden soil is best for in-ground planting. For containers, use potting mix which provides better drainage and aeration.
Soil Calculation Report
Your personalized soil calculation results
Project Details
Calculation Results
The tool is designed to be user-friendly, with easy-to-follow instructions to help you through each step of the calculation process. Get real-time results, adjust your measurements, and see how different factors, like soil depth or shape, affect the amount of soil you need. It’s an essential tool for anyone looking to take the guesswork out of their garden or landscaping project.
Advanced Resources and Further Reading

In-Depth Guides:
Now that you’ve got the basics of soil calculation down, you might be curious to dive deeper into some related topics. There’s a lot more to soil than just volume, and understanding the finer details can make a huge difference in the success of your gardening or landscaping projects.
Soil Science: Dive into the world of soil science to better understand soil properties, types, and how they affect plant growth. Knowing your soil’s structure and composition can help you choose the right plants and amendments for your garden.
Soil Health: Understand the role of microorganisms in soil health and their impact on plant growth. Healthy soil is key to sustaining long-term plant growth and can be improved with the right mix of organic matter and careful soil management.
Soil Amendments: Explore the different types of soil amendments like compost, mulch, and organic fertilizers. Understanding how to amend your soil properly can improve its texture, drainage, and fertility, ensuring better plant health.
Soil pH Adjustment: The pH of your soil affects nutrient availability and plant growth. Learn how to measure and modify your soil's pH to create the best conditions for plant growth.
Glossary of Soil and Gardening Terms
If you're new to gardening or landscaping, some terms can get a bit overwhelming. A soil glossary can be a handy reference to keep around. Whether you’re figuring out what "bulk density" means or learning the difference between "silt" and "loam," understanding the language of soil can help you make more informed decisions.
By deepening your knowledge of soil, you’ll gain more confidence in using your soil calculator and applying the right materials to create healthy, thriving gardens and landscapes. Happy gardening!
Conclusion
Using a soil calculator isn’t just about getting numbers—it’s about making your gardening, landscaping, or construction projects easier, more cost-effective, and ultimately more successful. By measuring accurately, inputting your data correctly, and adjusting for real-world factors like compaction, you can ensure that you’re using the right amount of soil for your needs. Whether you're planting a simple flower bed or designing a large backyard landscape, the soil calculator will save you time and money while helping your plants thrive.
So, the next time you're working on a project, big or small, take a moment to use the soil calculator. It’s a simple tool that can make all the difference in how your plants grow and how smoothly your project goes. Don't skip this step—it’s an easy way to set yourself up for success.
Now that you know how to calculate soil accurately, why not explore other gardening and landscaping tips to make your projects even more rewarding? From soil health to planting tips, there’s always more to learn. Keep experimenting, and enjoy the process of bringing your outdoor spaces to life!
Take the next step—use the calculator, plan your space, and watch your garden grow!
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
How do I calculate how much soil I need?
To figure out how much soil you need, measure the length, width, and depth of the space you plan to fill. Multiply these dimensions to get the volume in cubic units (like cubic feet or cubic yards). A soil calculator can help make this process quick and accurate, so you don’t have to do the math by hand.
What dimensions do I need to input into a soil calculator?
For most calculations, you'll need the length, width, and depth of the area you're working with. For irregular areas, like circles or sloped spaces, you may need to modify your measurements or break the area into easier shapes. The more precise your measurements, the more accurate your result will be.
How do I convert cubic feet to cubic yards?
To convert cubic feet to cubic yards, divide the number of cubic feet by 27 (since there are 27 cubic feet in a cubic yard). For example, if you have 54 cubic feet, divide 54 by 27 to get 2 cubic yards.
How many bags of soil will I need for my garden bed?
To estimate how many bags of soil you’ll need, first calculate the total volume of soil required (in cubic feet or yards). Then, check the bag size—typically, a standard bag holds 1 cubic foot. Divide the total volume by the size of the bag to get the number of bags you need. Soil calculators can make this conversion easy for you.
What is the best soil type for my project?
The best soil type depends on your project. For general gardening, loam is ideal because it drains well but retains moisture. For plants that need more water retention, like vegetables, a mix of loam and compost is perfect. Sandy soil drains quickly but may need amendments to hold nutrients. Clay soil holds moisture but can become compacted, so you may need to add organic material for better drainage.
How do I calculate soil for irregular or sloped areas?
For irregular areas, break them down into smaller shapes—rectangles, circles, or triangles—and calculate each part separately. For sloped areas, measure the depth at various points and use the average depth for your calculation. A soil calculator can help simplify these processes and account for tricky shapes.
Can I use a soil calculator for mulch, gravel, or compost?
Yes! You can use a soil calculator for mulch, gravel, or compost by inputting the same measurements as you would for soil. Most calculators offer an option to switch between different materials, and they can adjust the volume based on the type of material you're using.
How accurate are soil calculators?
Soil calculators are pretty accurate, but the accuracy depends on how precise your measurements are. Always double-check your dimensions and consider adding a little extra for compaction or settling, especially if you're using loose, organic soil mixes.
Check More Calculator